Sun-Grown vs Indoor: Two cultivation methods dramatically impact Blue Cannabis Strains. Outdoor sun exposure enhances plant development, intensifying blue hues and terpene profiles, boosting therapeutic benefits but facing weather & pest challenges. Indoor cultivation provides year-round control over climate, light spectra, and yield, optimizing growth yet demanding significant upfront investments. Each method shapes the visual, sensory, and medicinal characteristics of Blue Cannabis Strains differently, catering to diverse consumer preferences.
In the growing cannabis industry, understanding the nuances of sun-grown versus indoor cultivation is paramount for cultivators and consumers alike. This article delves into the benefits and drawbacks of each method, exploring how environmental factors shape plant development. We also shine a spotlight on the emerging role of blue cannabis strains in these growth methods, examining their unique properties and potential advantages. By weighing pros and cons, this guide offers valuable insights for both seasoned cultivators and curious consumers.
- Sun-Grown Cannabis: The Benefits and Drawbacks
- Indoor Cannabis Cultivation: Pros and Cons
- Exploring the Impact of Blue Cannabis Strains in Growth Methods
Sun-Grown Cannabis: The Benefits and Drawbacks

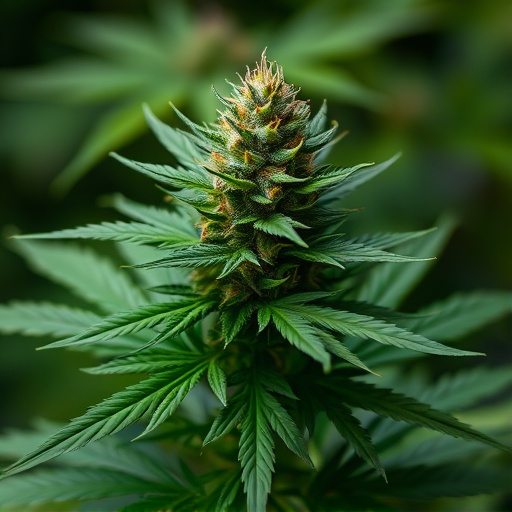
Sun-Grown Cannabis offers a unique set of advantages and challenges for cultivators and consumers alike. One of its key benefits is exposure to natural sunlight, which can enhance the development of desirable traits in cannabis plants, particularly in blue cannabis strains known for their therapeutic properties and distinct flavors. Sunlight stimulates photosynthesis, promoting robust growth and often resulting in higher cannabinoid concentrations, including THC and CBD. This natural process can create a diverse range of terpene profiles, contributing to the overall aroma and potential therapeutic effects.
However, outdoor cultivation is not without drawbacks. Unpredictable weather conditions, such as extreme temperatures, rain, or frost, can damage crops and reduce yield. Pests and diseases are also more prevalent in open-air environments, requiring meticulous monitoring and sustainable pest management practices. Additionally, securing a consistent supply of sun-grown cannabis might be challenging, as it relies on seasonal growth cycles, which can limit year-round availability.
Indoor Cannabis Cultivation: Pros and Cons

Indoor cannabis cultivation offers a controlled environment for growing high-quality plants, year-round. Pros include consistent climate control, reduced pest and disease pressure, and the ability to optimize light spectra for specific blue cannabis strains, enhancing their therapeutic properties. Advanced lighting technologies allow farmers to manipulate growth cycles, leading to faster flowering times and higher yields. This method is particularly appealing for commercial growers aiming to meet market demands efficiently.
However, indoor cultivation also presents several challenges. High energy costs associated with lighting and climate control can significantly impact profitability. Additionally, the lack of natural sunlight may result in lower overall plant health and reduced terpene profiles compared to sun-grown cannabis. Indoor operations require extensive setup and maintenance, demanding significant upfront investments in equipment and infrastructure. These factors make indoor cultivation less accessible for small-scale growers or those with limited resources.
Exploring the Impact of Blue Cannabis Strains in Growth Methods

Blue cannabis strains, known for their unique visual appeal and diverse chemical profiles, offer a compelling contrast when compared to traditional sun-grown or indoor cultivation methods. The impact of growth conditions on these strains is significant, as they tend to express distinct characteristics based on whether they are grown outdoors in natural sunlight or inside controlled environments.
In outdoor settings, blue cannabis plants often develop deeper blue hues and more robust terpene profiles due to the varying light spectrum and duration throughout the day. This method allows for a more natural development of the plant’s chemistry, which can lead to strains with potent therapeutic benefits. On the other hand, indoor cultivation offers precise control over environmental factors, enabling cultivators to optimize conditions for specific blue strain traits, such as increased yields or enhanced flavor compounds. The choice between sun-grown and indoor cultivation thus influences not only the visual aesthetics of blue cannabis but also its sensory profile and potential medicinal properties.
In conclusion, both sun-grown and indoor cannabis cultivation methods offer unique advantages and drawbacks. Sun-grown cannabis benefits from natural sunlight, leading to potent plants and a more environmentally friendly approach, but it’s limited by geographical constraints and seasonal variations. Indoor cultivation provides year-round control over environmental factors, enabling precise optimization for optimal plant growth, though it demands significant investment in equipment and energy. The exploration of blue cannabis strains further expands these options, potentially enhancing medicinal properties and offering diverse consumer experiences. Ultimately, the choice between sun-grown and indoor cannabis depends on specific needs, available resources, and desired outcomes, be it flavor, potency, or sustainability.